Spraying Soybeans
Many student pollinators, like bumblebees, build regular visits to soybeans and square measure at danger from pesticide sprays.As we have a tendency to get near soybeans flowering in Ohio (growth stages R1-R2), we\’d like to say a crucial issue connected not specifically to honeybees, however to pollinators generally (albeit honeybees in soybeans remains a concern). though soybeans square measure a autogamic crop, student pollinators like bumblebees and different solitary bees do visit soybean fields often throughout the crop’s flowering stage. These pollinators will visit different near sites, giving pollinating services to different plants together with flowers and if gift, vegetable crops. analysis out of Iowa State University indicates that several student pollinators build regular visits to soybeans and square measure at danger from pesticide sprays; researchers at the OARDC have recently joined these studies.
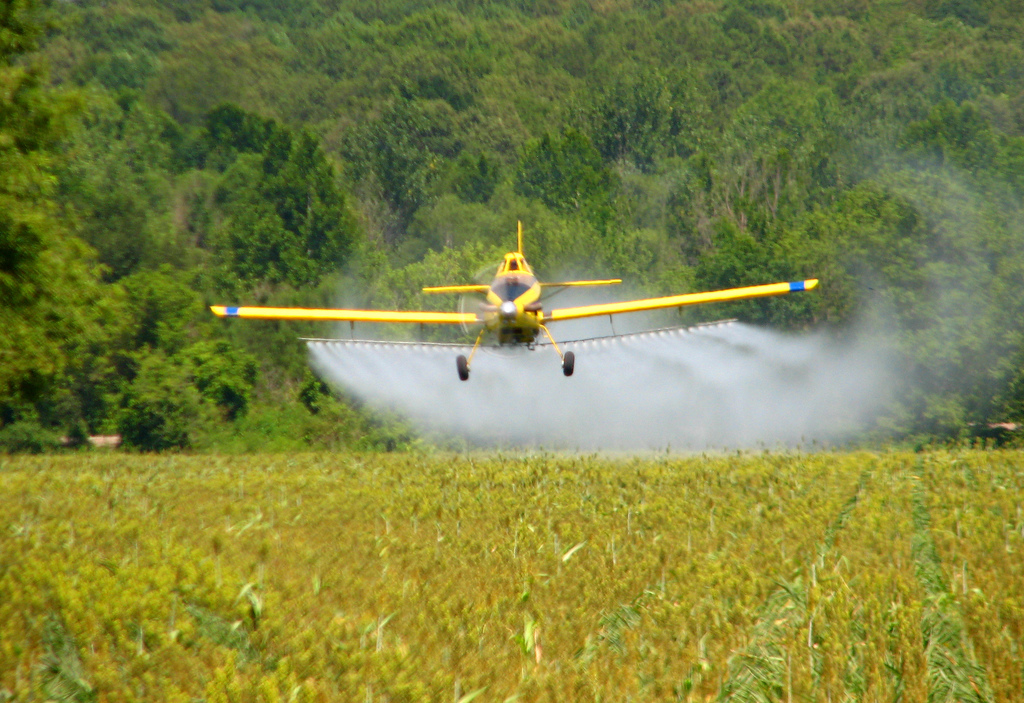
Luckily, there square measure few insect pests that reach economic levels throughout flowering in Ohio; the majority occur throughout pod development or seed fill stages (R3-R5). Thus, once following associate IPM strategy, very little pesticide ought to be sprayed at flowering as a result of a treatment application, as we have a tendency to all apprehend, ought to solely be applied once required, once a threshold is reached, and not applied as a preventive application.
However, we have a tendency to square measure aware that several growers square measure adding pesticides to spray tanks once applying fungicides for plant health functions and even late applications of herbicides because: \”Well, I’m going over the sector associateyway therefore i assumed I’d add an pesticide for insurance functions. The pesticide is comparatively low cost and thereforeybeans square measure price so much!\” As we\’ve forever declared, we have a tendency to don\’t advocate this observe, associated feel an IPM approach is far higher for everybody and everything, together with the surroundings and during this case, pollinators. we have a tendency to ne\’er advocate associate pesticide application unless there\’s a requirement. And with the recent data and concern concerning student pollinators, this caution is even a lot of necessary.
To illustrate this potential drawback, simply time period agone there was a big bee kill in Beaver State, once over fifty,000 bumblebees were killed by associate pesticide sprayed (in this case a fabric referred to as Safari) on linden trees during a parking zone throughout a period of time once the trees were in flower and being visited by bumblebees (read only one of the various articles that were written concerning this). This was with associate pesticide that had the warning concerning being extremely deadly to bees on its label and therefore the got to NOT spray flowering plants or trees.
Growers and applicators ought to keep in mind, having browse the label, that almost all pesticides have a press release concerning spraying around bees and on blooming crops. the standard statement is: \”This product is extremely deadly to bees exposed to direct treatment or residues on blooming crops or weeds. don\’t apply this product or permit it to drift to blooming crops or weeds if bees square measure actively visiting the treatment space.\” ensure you\’re acquainted with your state laws before spraying.
We still advise that growers and applicators maintain smart communications with bee keepers close to their fields to stop and limit unwitting issues. an inventory of registered apiaries will probably be obtained from your state\’s executive department.
Applicators ought to avoid spraying once bees square measure active within the field with flowering crops or weeds. different times to avoid spraying square measure from ten a.m. to 7 p.m. or once temperatures square measure on top of sixty five degrees F. On extraordinarily hot days, bees is also active later into the evening.
Follow label precautions that relate to drift and bear in mind of the potential risk to neighboring crops or areas. Filter strips or different conservation areas that border fields might have flowering plants with forage bees. Bees have a protracted vary and might forage up to 2 and half miles from the shed.

Thanks for installing the Bottom of every post plugin by Corey Salzano. Contact me if you need custom WordPress plugins or website design.